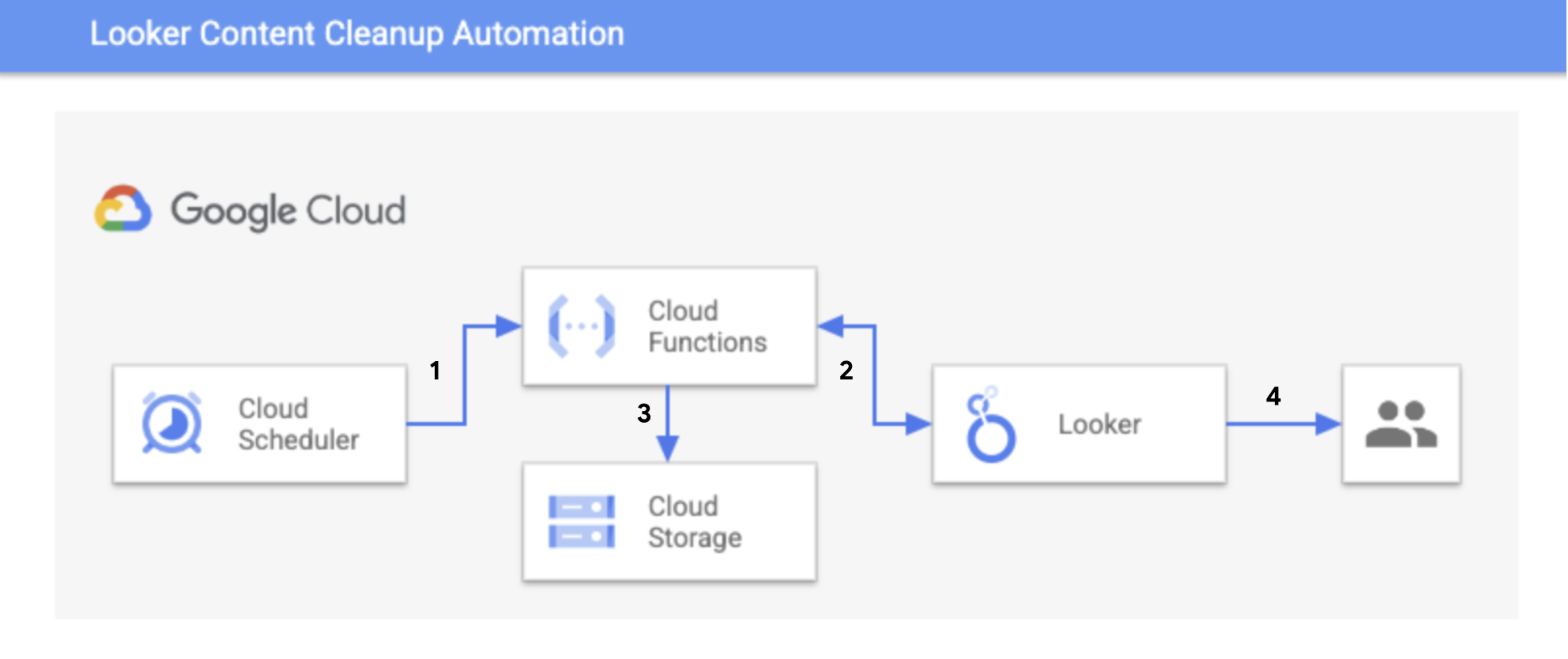
This repository contains a Google Cloud Function that leverages the Looker Python SDK to automate Looker content cleanup. It can be triggered to run at your desired cadence using Cloud Scheduler.
Implementing an automated content cleanup process will help your instance avoid content bloat and make users more productive when searching for content. Content bloat is the effect on an organization when time is wasted finding the relevant content to answer a question or recreating content that already exists.
The cleanup process implemented by this script is as follows:
- Schedule content clean up automation to run every 90 days (default).
- Dashboards and Looks not used in the past 90 days (default) are archived (soft deleted). Soft deleting a piece of content means moving it to the Trash folder which only admins have access to.
- Soft deleted content can be restored to its original folder from either the UI or with the API (Appendix).
- Permanently delete content (i.e. remove from Trash folder) that's been soft-deleted and goes unclaimed for another 90 days (default). Before permanently deleting dashboards, the dashboard LookML is saved to a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
- Permanently deleted dashboards which were backed up before deletion can be restored using the import_dashboard_from_lookml method.
⚠️ WARNING: Permanently deleted content is lost forever. You cannot undo this action!
Running the automation every 90 days allows the script to handle both soft-deleting and permanently deleting content at the same time. That said, the days are configurable within the script.
NOTE: this automation only works for Looks and user-defined dashboards. The unused content email notification will contain LookML dashboards which can be deleted by removing their dashboard lkml file in their LookML project.
- Trigger automation at desired interval
- Run queries and update content
- Backup dashboards before permanent deletion
- Send unused content and deleted content email notification
- Looker instance in which you have Admin permissions.
- Google Cloud Project with the following APIs enabled:
- Artifact Registry API
- Cloud Run Admin API
- Cloud Build API
- Cloud Functions API
- Cloud Logging API
- Cloud Pub/Sub API
- Cloud Scheduler API
- Secret Manager API
- Cloud Storage API
The script executes the following steps each time it is run:
- Get two query IDs which run a System Activity query to identify content unused in the past 90 days (default) and content deleted more than 90 days ago (default), respectively.
- Run both queries to get data for unused content and deleted content.
- Soft delete unused content.
- Permanently delete content in Trash folder.
- Dashboards will be backed up to a GCS bucket before being deleted. Backups are not available for Looks.
- Send two emails containing the soft deleted and permanently deleted content in CSV format.
- Delivery format can be updated on line 185 of main.py to any of the accepted formats.
The script is currently in dry run / safe mode to avoid accidental content deletions while setting up this automation. This means the soft delete and hard delete functions are commented out in main.py (soft_delete_dashboard, soft_delete_look, hard_delete_dashboard, hard_delete_look).
In dry run mode, the automation will run the queries, send the schedules, and backup dashboards that are to be hard deleted without actually deleting any content.
In main.py search todo to:
- Update
GCP_PROJET_IDandGCS_BUCKET_NAMEto enable backing up dashboards to GCS before permanent deletion. - Update
DAYS_BEFORE_SOFT_DELETE(# of days content is unused before archival) andDAYS_BEFORE_HARD_DELETE(# of days in trash before permanently deletion). - Update
NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS(email address for content deletion notification). - Toggle dry run of automation off/on depending on if you want content to be deleted.
Before deploying to production, please abide by the principle of least privilege and modify the service account used for this automation to meet your company's security standards and has their approval.
The following steps assume deployment using the Google Cloud UI Console.
-
Obtain a Looker API3 Key.
-
In
main.pyupdate: -
Go to Cloud Secret Manager and enable the Secret Manager API. Create the following secrets:
looker-base-url: secret value is your Looker instance URL (e.g.https://my_looker_instance.cloud.looker.com/)looker-client-id: secret value is the Client ID generated in Step 1.looker-client-secret: secret value is the Client Secret generated in Step 1.
-
Go to Cloud Storage and create a new bucket.
-
Cloud Storage bucket suggested settings, modify as necessary:
-
Name your bucket:
looker-automation-dashboards-backup- Update
GCS_BUCKET_NAMEwith this value on line 32 of main.py. - Select
Continue
- Update
-
Choose where to store your data
- Location type:
Region,us-west1 (Oregon)(or preferred type & region) - Select
Continue
- Location type:
-
Choose a storage class for your data
Set a default class-->ColdlineorArchive- Select
Continue
-
Choose how to control access to objects
- Prevent public access:
Enabled - Access control:
Uniform - Select
Continue
- Prevent public access:
-
Select
Create
-
-
Go to Cloud Functions and create a new function.
-
Cloud Functions function suggested settings, modify as necessary:
-
Basics
- Environment:
2nd gen - Function name:
looker-content-cleanup-automation - Region:
us-west1(or preferred region) - Authentication:
Require authentication - Require HTTPS:
Enabled - Select
Save
- Environment:
-
Runtime, build, connections and security settings
-
Runtime
- Memory allocated:
512 MB - Timeout:
3600 - Runtime service account:
App Engine default service account
- Memory allocated:
-
Security and Image Repo
- Reference a Secret: reference the
looker-base-urlsecret created in Step 3 and map it to theLOOKERSDK_BASE_URLenvironment variable.- Secret:
looker-base-url - Reference method:
Exposed as environment variable - Name 1:
LOOKERSDK_BASE_URL - Select
Done
- Secret:
- Reference a Secret: reference the
looker-client-idsecret created in Step 3 and map it to theLOOKERSDK_CLIENT_IDenvironment variable.- Secret:
looker-client-id - Reference method:
Exposed as environment variable - Name 1:
LOOKERSDK_CLIENT_ID - Select
Done
- Secret:
- Reference a Secret: reference the
looker-client-secretsecret created in Step 3 and map it to theLOOKERSDK_CLIENT_SECRETenvironment variable.- Secret:
looker-client-secret - Reference method:
Exposed as environment variable - Name 1:
LOOKERSDK_CLIENT_SECRET - Select
Done
- Secret:
- Reference a Secret: reference the
-
Select
Next
-
-
Code
- Runtime:
Python 3.9 - Copy and paste the contents of
main.pyin this repository into themain.pyfile once inside Cloud Function's inline editor. - Entry point:
main- NOTE: review the
todoitems listed in the script prior to deploying, otherwise the automation won't work as intended.
- NOTE: review the
- Copy and paste the contents of
requirements.txtin this repository to therequirements.txtfile once inside Cloud Function's inline editor.
- Runtime:
-
Deploy the function.
-
-
Go to Cloud IAM > IAM and grant the
App Engine default service account(<project-name>@appspot.gserviceaccount.com) principal:Secret Manager Secret Accessorrole to access the secrets created in Step 2.Storage Object Creatorrole to backup dashboards to the GCS bucket created in Step 5.
-
Test the automation function in dry run mode (run queries, backup dashboards, and send schedules, without soft deleting or hard deleting any content).
- Check out this article for detailed instructions.
-
Go to Cloud Scheduler and select
Schedule a job(orCreate job). -
Cloud Scheduler job suggested settings, modify as necessary:
-
Define the schedule
- Name:
trigger-looker-content-cleanup-automation - Region:
us-west1 (Oregon)(same region as Cloud Function) - Frequency:
0 0 1 */3 *(every 3 months or update to desired frequency of how often the automation should run) - Timezone: Select desired timezone the scheduled job should use
- Select
Continue
- Name:
-
Configure the execution
- Target type:
HTTP - URL: Trigger URL from function created in Step 4
- HTTP method:
POST - Auth header:
Add OIDC token - Service account:
App Engine default service account
- Target type:
-
Select
Create
-
-
Test the schedule (Actions > Force run) to confirm it triggers the
looker-content-cleanup-automationfunction in dry run mode. -
After validating everything is working as expected, make the
todochanges tomain.pyto toggle off dry run mode.
import looker_sdk
from looker_sdk import models40
config_file = "looker.ini"
sdk = looker_sdk.init40(config_file)
def restore_soft_delete_dashboard(dashboard_id):
dashboard = models40.WriteDashboard(deleted=False)
try:
sdk.update_dashboard(str(dashboard_id), body=dashboard)
print(f"Successfully restored dashboard {dashboard_id}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
def restore_soft_delete_look(look_id):
look = models40.WriteLookWithQuery(deleted=False)
try:
sdk.update_look(str(look_id), body=look)
print(f"Successfully restored look {look_id}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# Provide a list of look_ids to restore
looks_to_restore = []
for look in looks_to_restore:
restore_soft_delete_look(look)
# Provide a list of dashboard_ids to restore
dashboards_to_restore = [1]
for dashboard in dashboards_to_restore:
restore_soft_delete_dashboard(dashboard)