A Python library for GraphSLAM implemented in Rust.
This was originally written in Python using scipy.sparse and scipy.optimize.minimize but was rewritten in Rust for two reasons:
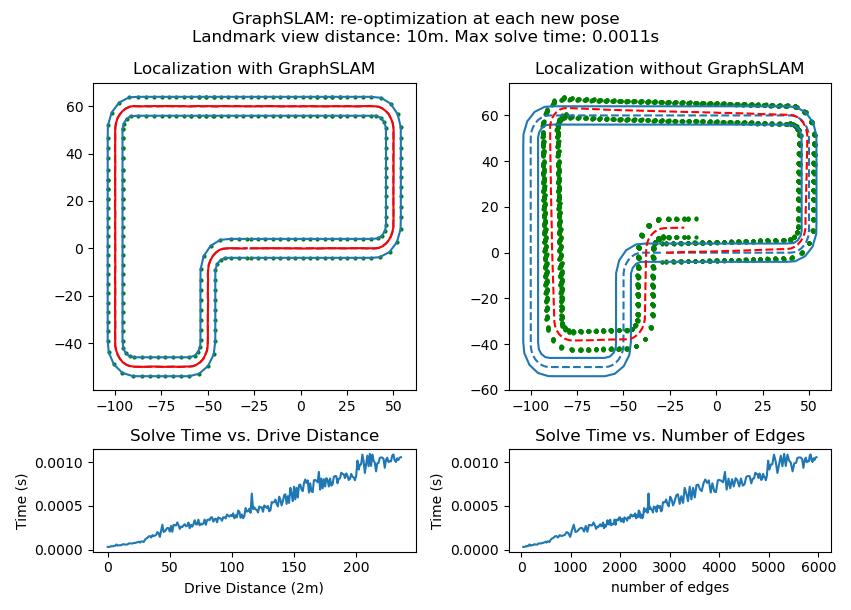
- speed. Even with everything done using numpy broadcasting or scipy functions, the Rust implementation is at least 3x faster for the ~6000 edge test case.
- learning. I read about the Maturin.rs packaging framework for pyo3 python bindings, and I wanted to try it out.
The current implementation keeps track of everything using a custom sparse matrix struct that uses the triplet format. To solve, the matrix is loaded into a CSPARSE matrix and converted to Compressed Column format. This implementation of graphslam is purely linear, so it boils down to a linear least squares problem:
The solve itself is performed in two steps:
- compute
$A^\intercal A$ and$A^\intercal b$ - solve the symmetric positive definite system
$A^\intercal A\setminus A^\intercal b$ using the Cholesky decomposition
I don't know why, but this is significantly faster than the builtin cs_qrsol CSPARSE method to solve the linear least squares problem. I saw this in scipy.sparse as well.
I'm currently looking into switching to one of the HSL linear solvers (either MA27 or MA57), since I've had a lot of success using those with IPOPT, but I need to figure out how to compute
Every time we get new landmarks from vision, we try to match them to the known landmarks by rotating and translating them optimally. I use the FiniteDiff crate to compute the derivatives, and just a simple newton's method to optimize.
It's meant to be coarse and fast, not precise.