-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 95
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
4 changed files
with
124 additions
and
1 deletion.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
121 changes: 121 additions & 0 deletions
121
docs/front-end-basic/performance/front-end-performance-task-schedule.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,121 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| title: 前端性能优化--任务管理和调度 | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| 对于一个前端应用,最理想的性能便是任何用户的交互都不会被阻塞、且能及时得到响应。 | ||
|
|
||
| 显然,当我们应用程序里需要处理一些大任务计算的时候,这个理想状态是难以达到的。不过,努力去接近也是我们可以尽量去做好的。 | ||
|
|
||
| # 任务调度与性能 | ||
|
|
||
| 任务调度的出现,基本上是为了更合理地使用和分配资源。在前端应用中,用户的交互则是最高优先级需要响应的,用户操作是否能及时响应,往往是我们衡量一个前端应用是否性能好的重要标准。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 浏览器的“一帧” | ||
|
|
||
| 前面在[《前端性能优化--卡顿心跳检测》](./front-end-performance-jank-heartbeat-monitor.mdr)一文中,我们提到说使用`requestAnimationFrame`来检测是否产生了卡顿。除此之外,如果你也处理过简单的异步任务管理(闲时执行等),或许你还用过`requestIdleCallback`。 | ||
|
|
||
| 其实,`requestAnimationFrame`和`requestIdleCallback`都会在浏览器的每一帧中被执行到。我们来看[下图](https://aerotwist.com/blog/the-anatomy-of-a-frame/): | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 每次浏览器渲染的过程顺序为: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. 用户事件。 | ||
| 2. 一个宏任务。 | ||
| 3. 队列中全部微任务。 | ||
| 4. `requestAnimationFrame`。 | ||
| 5. 浏览器重排/重绘。 | ||
| 6. `requestIdleCallback`。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们常用的事件监听的顺序则是[如图](https://medium.com/@paul_irish/requestanimationframe-scheduling-for-nerds-9c57f7438ef4): | ||
|
|
||
| 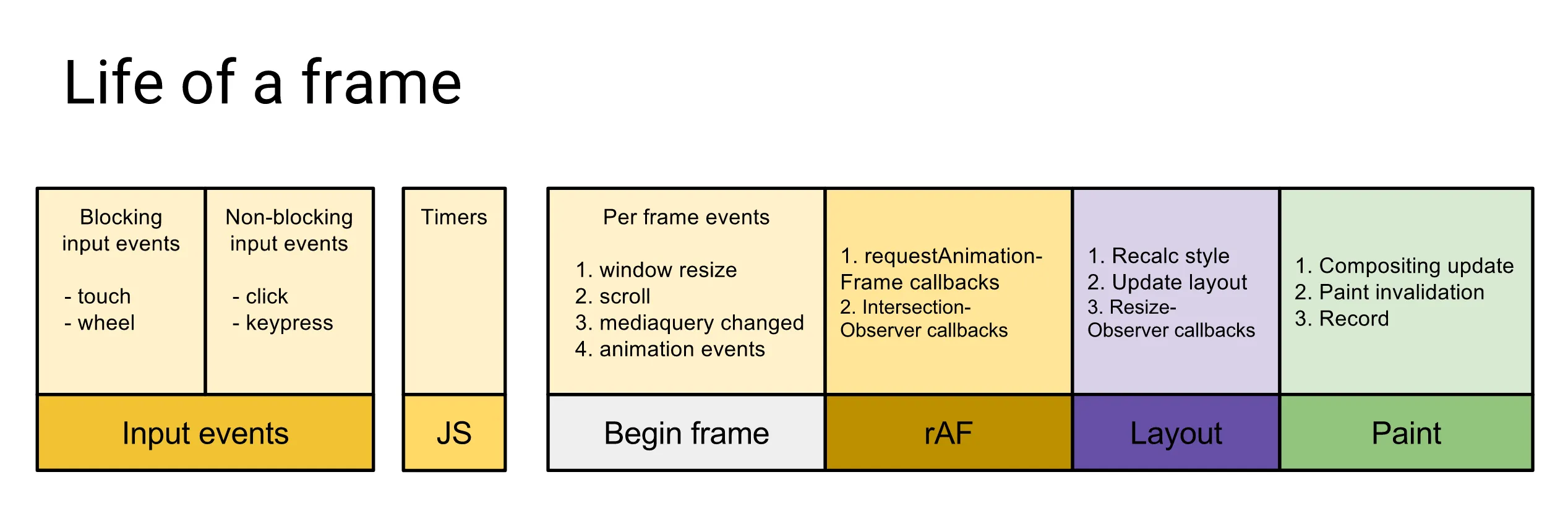 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 任务切片 | ||
|
|
||
| 之前在[《让你的长任务在 50 毫秒内结束》](./front-end-performance-long-task.md)一文中说过:RAIL 的目标是在 100 毫秒内完成由用户输入发起的转换,让用户感觉互动是瞬时完成的。 | ||
|
|
||
| 为确保在 100 毫秒内获得可见响应,RAIL 的准则是在 50 毫秒内处理用户输入事件,这也是为什么我们使用`requestIdleCallback`处理空闲回调任务时,`timeRemaining()`有一个 50ms 的上限时间。 | ||
|
|
||
| 好的任务调度可以让页面不会产生卡顿,这个前提是每个被调度的任务的颗粒度足够细,也可理解为单个任务需要满足下述两个条件之一: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. 在 50ms 内执行完成。 | ||
| 2. 支持暂停以及继续执行。 | ||
|
|
||
| 对于希望尽可能达到理想状态的系统来说,要让所以可拆卸的任务满足上述条件,都才是最难实现的部分。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 切片后任务执行 | ||
|
|
||
| 只要任务可控制在 50ms 内结束或者中断再恢复,那么我们就可以很简单地利用浏览器的每一帧渲染过程,来实现“不会产生卡顿”的任务管理。 | ||
|
|
||
| 最简单的,我们可以设置每一次执行的耗时上限,当每个任务执行完之后,检测一下本次执行耗时,超过 50ms 则通过定时器或是`requestAnimationFrame`、`requestIdleCallback`等方法,将剩余任务放到下一次渲染前后处理。 | ||
|
|
||
| 比如之前[《复杂渲染引擎架构与设计--分片计算》](../render-engine/render-engine-calculate-split.md)一文中提到的,简单的`setTimeout`便能使任务执行不阻塞用户操作: | ||
|
|
||
| ```ts | ||
| class AsyncCalculateManager { | ||
| // 每次执行任务的耗时 | ||
| static timeForEveryTask = 50; | ||
|
|
||
| /** | ||
| * 跑下一次任务 | ||
| */ | ||
| private runNext() { | ||
| if (this.timer) clearTimeout(this.timer); | ||
|
|
||
| this.timer = setTimeout(() => { | ||
| // 一个任务跑 50 ms | ||
| const calculateRange = this.calculateRunner.calculateNextTask( | ||
| AsyncCalculateManager.timeForEveryTask | ||
| ); | ||
|
|
||
| // 处理完之后,剩余任务做异步 | ||
| this.runNext(); | ||
| }, 10); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 除此之外,`requestAnimationFrame`适合处理影响页面渲染(比如操作 DOM)的任务,而`requestIdleCallback`可以处理与页面渲染无关的一些计算任务。 | ||
|
|
||
| 当然,常见的任务调度还需要支持这些能力: | ||
|
|
||
| - 定义任务优先级 | ||
| - 并行/串行/顺序执行任务 | ||
|
|
||
| 在前端应用中,大家都比较认可和熟知的任务调度便是 React 虚拟 DOM 的计算,我们可以来看看。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## React 虚拟 DOM 与任务调度 | ||
|
|
||
| React 中使用协调器(Reconciler)与渲染器(Renderer)来优化页面的渲染性能。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们都知道在 React 里,可以使用`ReactDOM.render`/`this.setState`/`this.forceUpdate`/`useState`等方法来触发状态更新,这些方法共用一套状态更新机制,该更新机制主要由两个步骤组成: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. 找出变化的组件,每当有更新发生时,协调器会做如下工作: | ||
|
|
||
| - 调用组件 render 方法将 JSX 转化为虚拟 DOM | ||
| - 进行虚拟 DOM Diff 并找出变化的虚拟 DOM | ||
| - 通知渲染器 | ||
|
|
||
| 2. 渲染器接到协调器通知,将变化的组件渲染到页面上。 | ||
|
|
||
| 在 React15 及以前,协调器创建虚拟 DOM 使用的是递归的方式,该过程是无法中断的。这会导致 UI 渲染被阻塞,造成卡顿。为此,React16 中新增了调度器(Scheduler),调度器能够把可中断的任务切片处理,能够调整优先级,重置并复用任务。 | ||
|
|
||
| 调度器会根据任务的优先级去分配各自的过期时间,在过期时间之前按照优先级执行任务,可以在不影响用户体验的情况下去进行计算和更新。 | ||
|
|
||
| 简单来说,最重要的依然是两个步骤: | ||
|
|
||
| - 时间切片:将更新中的 render 阶段划分一个个的小任务,通常来说这些小任务连续执行的最长时间为 5ms | ||
| - 限制时间执行任务:每次执行小任务,都会记录耗时,如果超过 5ms 就跳出当前任务,并设置一个宏任务开始下一轮事件循环 | ||
|
|
||
| 通过这样的方式,React 可在浏览器空闲的时候进行调度并执行任务。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 参考 | ||
|
|
||
| - [任务调度 Scheduler](https://www.qinguanghui.com/react/%E4%BB%BB%E5%8A%A1%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6.html) | ||
|
|
||
| # 结束语 | ||
|
|
||
| 任务调度其实很简单,无非就是将所有执行代码尽可能拆分为一个个的切片任务,并在浏览器每帧渲染前后处理一部分任务,从而达到不阻塞用户操作的目的。 | ||
|
|
||
| 但实际上这件事要做好来又是很困难的,需要将几乎整个应用程序都搭建于这套任务调度之上,并拆成足够小可执行的任务,往往这才是在项目中做好性能的最大难点。 |