The ReLU function, F(x)=max(0,x), returns x for all values of x > 0, and returns 0 for all values of x ≤ 0.
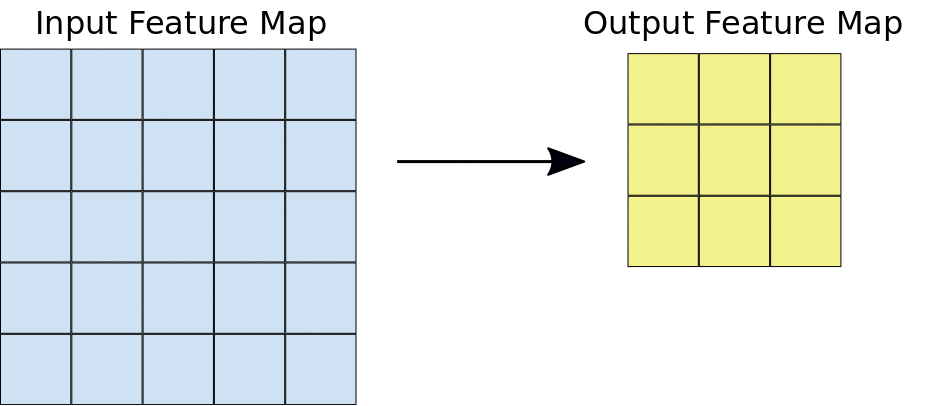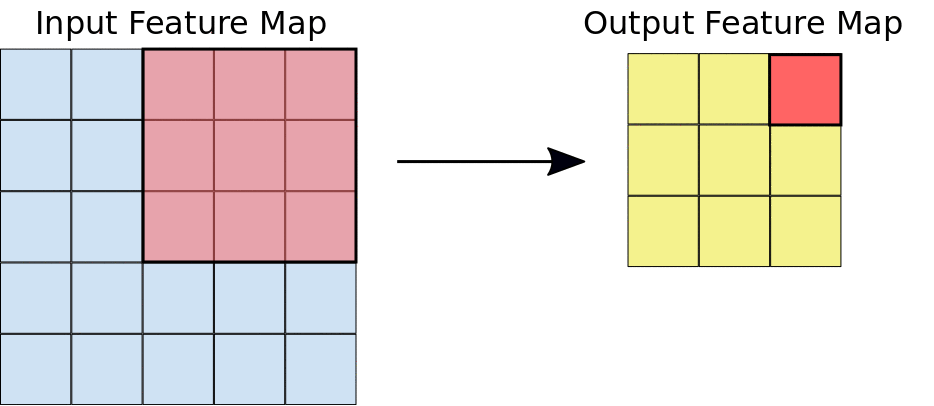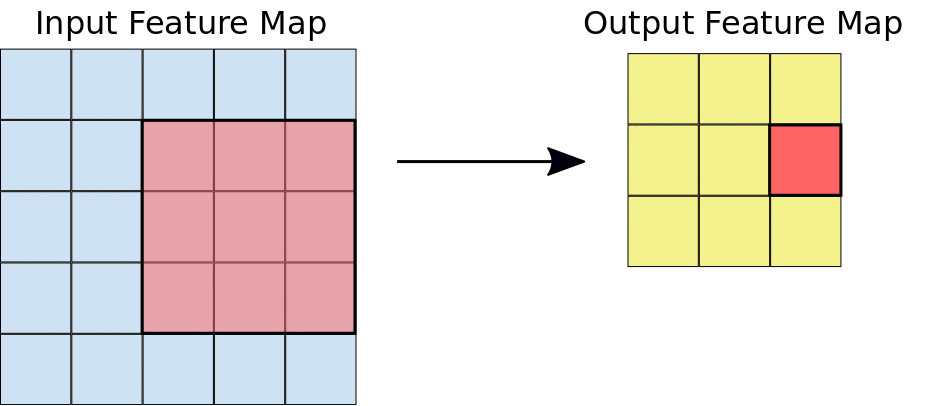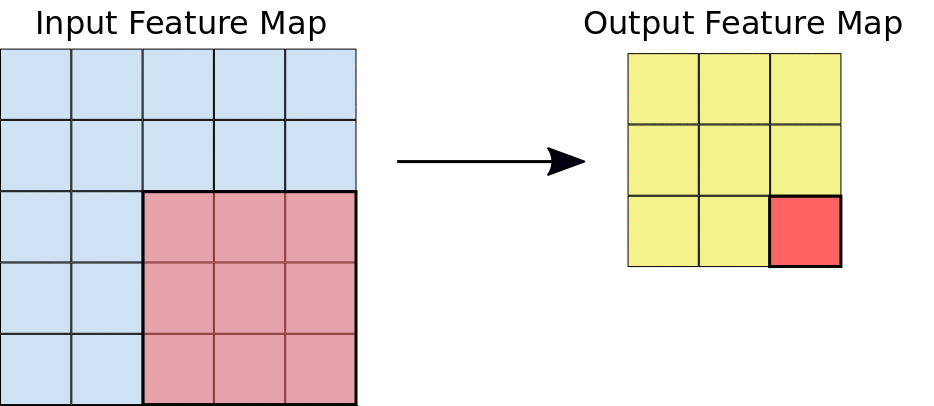
Size of the max-pooling filter (typically 2x2 pixels)
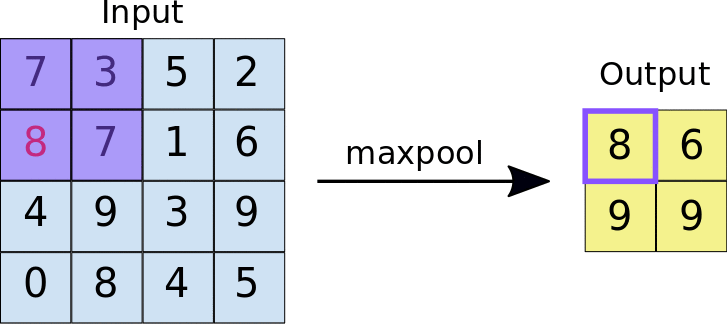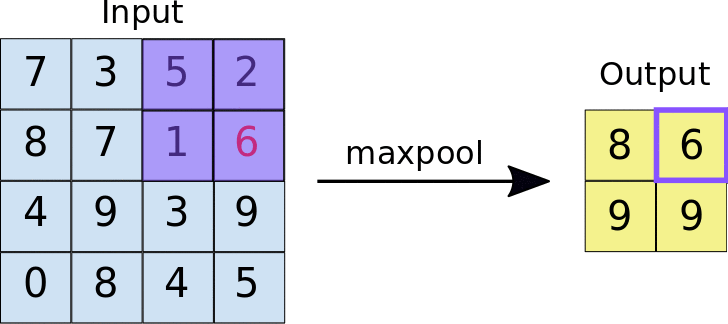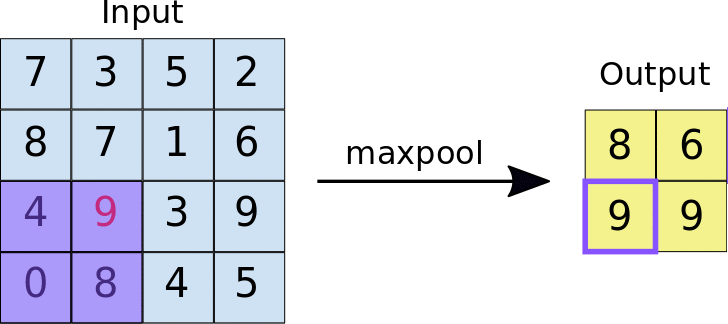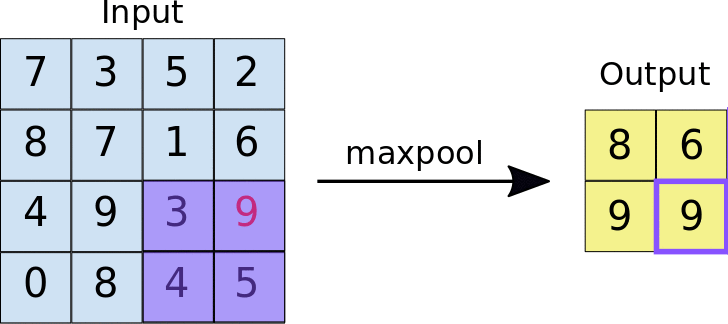
Stride: the distance, in pixels, separating each extracted tile. Unlike with convolution, where filters slide over the feature map pixel by pixel, in max pooling, the stride determines the locations where each tile is extracted. For a 2x2 filter, a stride of 2 specifies that the max pooling operation will extract all nonoverlapping 2x2 tiles from the feature map (see Figure 5).
artificially boosting the diversity and number of training examples by performing random transformations to existing images to create a set of new variants (see Figure 7). Data augmentation is especially useful when the original training data set is relatively small.
Randomly removing units from the neural network during a training gradient step.