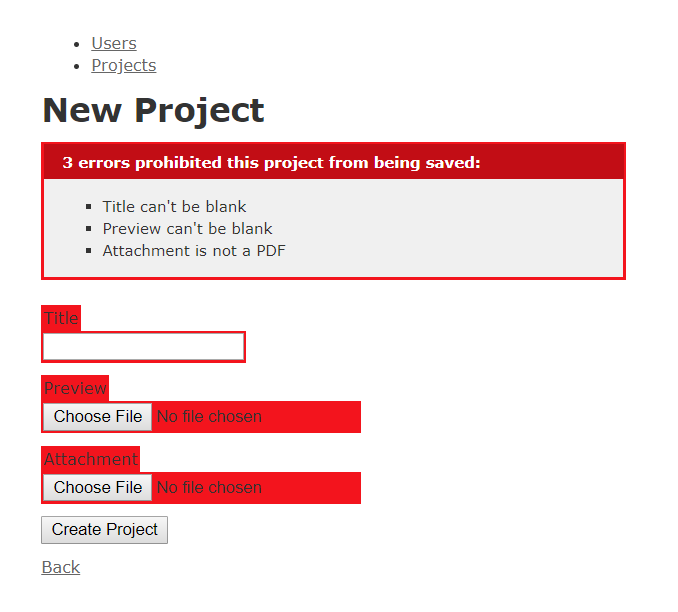
If you are using active_storage gem and you want to add simple validations for it, like presence or content_type you need to write a custom validation method.
This gems doing it for you. Just use attached: true or content_type: 'image/png' validation.
- validates if file(s) attached
- validates content type
- validates size of files
- validates total size of files
- validates dimension of images/videos
- validates number of uploaded files (min/max required)
- validates aspect ratio (if square, portrait, landscape, is_16_9, ...)
- validates if file can be processed by MiniMagick or Vips
- custom error messages
- allow procs for dynamic determination of values
For example you have a model like this and you want to add validation.
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
has_many_attached :photos
has_one_attached :image
validates :name, presence: true
validates :avatar, attached: true, content_type: 'image/png',
dimension: { width: 200, height: 200 }
validates :photos, attached: true, content_type: ['image/png', 'image/jpeg'],
dimension: { width: { min: 800, max: 2400 },
height: { min: 600, max: 1800 }, message: 'is not given between dimension' }
validates :image, attached: true,
processable_image: true,
content_type: ['image/png', 'image/jpeg'],
aspect_ratio: :landscape
endor
class Project < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :logo
has_one_attached :preview
has_one_attached :attachment
has_many_attached :documents
validates :title, presence: true
validates :logo, attached: true, size: { less_than: 100.megabytes , message: 'is too large' }
validates :preview, attached: true, size: { between: 1.kilobyte..100.megabytes , message: 'is not given between size' }
validates :attachment, attached: true, content_type: { in: 'application/pdf', message: 'is not a PDF' }
validates :documents, limit: { min: 1, max: 3 }, total_size: { less_than: 5.megabytes }
end- Content type validation using symbols or regex.
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
has_many_attached :photos
validates :avatar, attached: true, content_type: :png
# or
validates :photos, attached: true, content_type: [:png, :jpg, :jpeg]
# or
validates :avatar, content_type: /\Aimage\/.*\z/
endPlease note that the symbol types must be registered by Marcel::EXTENSIONS that's used by this gem to infer the full content type.
Example code for adding a new content type to Marcel:
# config/initializers/mime_types.rb
Marcel::MimeType.extend "application/ino", extensions: %w(ino), parents: "text/plain" # Registering arduino INO filesContent type spoofing protection
File content type spoofing happens when an ill-intentioned user uploads a file which hides its true content type by faking its extension and its declared content type value. For example, a user may try to upload a .exe file (application/x-msdownload content type) dissimulated as a .jpg file (image/jpeg content type).
By default, the gem does not prevent content type spoofing (prevent it by default is a breaking change that will be implemented in v2). The spoofing protection relies on both the linux file command and Marcel gem. Be careful, since it needs to load the whole file io to perform the analysis, it will use a lot of RAM for very large files. Therefore it could be a wise decision not to enable it in this case.
Take note that the file analyzer will not find the exactly same content type as the ActiveStorage blob (its content type detection relies on a different logic using content+filename+extension). To handle this issue, we consider a close parent content type to be a match. For example, for an ActiveStorage blob which content type is video/x-ms-wmv, the file analyzer will probably detect a video/x-ms-asf content type, this will be considered as a valid match because these 2 content types are closely related. The correlation mapping is based on Marcel::TYPE_PARENTS.
The difficulty to accurately predict a mime type may generate false positives, if so there are two solutions available:
- If the ActiveStorage blob content type is closely related to the detected content type using the
fileanalyzer, you can enhanceMarcel::TYPE_PARENTSmapping usingMarcel::MimeType.extend "application/x-rar-compressed", parents: %(application/x-rar)in theconfig/initializers/mime_types.rbfile. (Please drop an issue so we can add it to the gem for everyone!) - If the ActiveStorage blob content type is not closely related, you still can disable the content type spoofing protection in the validator, if so, please drop us an issue so we can fix it for everyone!
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
validates :avatar, attached: true, content_type: :png # spoofing_protection not enabled, at your own risks!
validates :avatar, attached: true, content_type: { with: :png, spoofing_protection: true } # spoofing_protection enabled
end- Dimension validation with
width,heightandin.
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
has_many_attached :photos
validates :avatar, dimension: { width: { in: 80..100 }, message: 'is not given between dimension' }
validates :photos, dimension: { height: { in: 600..1800 } }
end- Dimension validation with
minandmaxrange for width and height:
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
has_many_attached :photos
validates :avatar, dimension: { min: 200..100 }
# Equivalent to:
# validates :avatar, dimension: { width: { min: 200 }, height: { min: 100 } }
validates :photos, dimension: { min: 200..100, max: 400..200 }
# Equivalent to:
# validates :avatar, dimension: { width: { min: 200, max: 400 }, height: { min: 100, max: 200 } }
end- Aspect ratio validation:
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one_attached :avatar
has_one_attached :photo
has_many_attached :photos
validates :avatar, aspect_ratio: :square
validates :photo, aspect_ratio: :landscape
# you can also pass dynamic aspect ratio, like :is_4_3, :is_16_9, etc
validates :photos, aspect_ratio: :is_4_3
end- Proc Usage:
Procs can be used instead of values in all the above examples. They will be called on every validation.
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many_attached :proc_files
validates :proc_files, limit: { max: -> (record) { record.admin? ? 100 : 10 } }
endActive Storage Validations uses I18n for error messages. For this, add these keys in your translation file:
en:
errors:
messages:
content_type_invalid: "has an invalid content type"
file_size_not_less_than: "file size must be less than %{max_size} (current size is %{file_size})"
file_size_not_less_than_or_equal_to: "file size must be less than or equal to %{max_size} (current size is %{file_size})"
file_size_not_greater_than: "file size must be greater than %{min_size} (current size is %{file_size})"
file_size_not_greater_than_or_equal_to: "file size must be greater than or equal to %{min_size} (current size is %{file_size})"
file_size_not_between: "file size must be between %{min_size} and %{max_size} (current size is %{file_size})"
total_file_size_not_less_than: "total file size must be less than %{max_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"
total_file_size_not_less_than_or_equal_to: "total file size must be less than or equal to %{max_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"
total_file_size_not_greater_than: "total file size must be greater than %{min_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"
total_file_size_not_greater_than_or_equal_to: "total file size must be greater than or equal to %{min_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"
total_file_size_not_between: "total file size must be between %{min_size} and %{max_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"
limit_out_of_range: "total number is out of range"
image_metadata_missing: "is not a valid image"
dimension_min_inclusion: "must be greater than or equal to %{width} x %{height} pixel"
dimension_max_inclusion: "must be less than or equal to %{width} x %{height} pixel"
dimension_width_inclusion: "width is not included between %{min} and %{max} pixel"
dimension_height_inclusion: "height is not included between %{min} and %{max} pixel"
dimension_width_greater_than_or_equal_to: "width must be greater than or equal to %{length} pixel"
dimension_height_greater_than_or_equal_to: "height must be greater than or equal to %{length} pixel"
dimension_width_less_than_or_equal_to: "width must be less than or equal to %{length} pixel"
dimension_height_less_than_or_equal_to: "height must be less than or equal to %{length} pixel"
dimension_width_equal_to: "width must be equal to %{length} pixel"
dimension_height_equal_to: "height must be equal to %{length} pixel"
aspect_ratio_not_square: "must be a square image"
aspect_ratio_not_portrait: "must be a portrait image"
aspect_ratio_not_landscape: "must be a landscape image"
aspect_ratio_is_not: "must have an aspect ratio of %{aspect_ratio}"
image_not_processable: "is not a valid image"In several cases, Active Storage Validations provides variables to help you customize messages:
The keys starting with aspect_ratio_ support two variables that you can use:
aspect_ratiocontaining the expected aspect ratio, especially useful for custom aspect ratiofilenamecontaining the current file name
For example :
aspect_ratio_is_not: "must be a %{aspect_ratio} image"The content_type_invalid key has three variables that you can use:
content_typecontaining the exact content type of the sent filehuman_content_typecontaining a more user-friendly version of the sent file content type (e.g. 'TXT' for 'text/plain')authorized_typescontaining the list of authorized content typesfilenamecontaining the current file name
For example :
content_type_invalid: "has an invalid content type : %{content_type}, authorized types are %{authorized_types}"The keys starting with dimension_ support six variables that you can use:
mincontaining the minimum width or height allowedmaxcontaining the maximum width or height allowedwidthcontaining the minimum or maximum width allowedheightcontaining the minimum or maximum width allowedlengthcontaining the exact width or height allowedfilenamecontaining the current file name
For example :
dimension_min_inclusion: "must be greater than or equal to %{width} x %{height} pixel."The keys starting with file_size_not_ support four variables that you can use:
file_sizecontaining the current file sizemincontaining the minimum file sizemaxcontaining the maximum file sizefilenamecontaining the current file name
For example :
file_size_not_between: "file size must be between %{min_size} and %{max_size} (current size is %{file_size})"The keys starting with total_file_size_not_ support three variables that you can use:
total_file_sizecontaining the current total file sizemincontaining the minimum file sizemaxcontaining the maximum file size
For example :
total_file_size_not_between: "total file size must be between %{min_size} and %{max_size} (current size is %{total_file_size})"The limit_out_of_range key supports two variables that you can use:
mincontaining the minimum number of filesmaxcontaining the maximum number of files
For example :
limit_out_of_range: "total number is out of range. range: [%{min}, %{max}]"The image_not_processable key supports one variable that you can use:
filenamecontaining the current file name
For example :
image_not_processable: "is not a valid image (file: %{filename})"Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'active_storage_validations'
# Optional, to use :dimension validator or :aspect_ratio validator
gem 'mini_magick', '>= 4.9.5'
# Or
gem 'ruby-vips', '>= 2.1.0'And then execute:
$ bundleVery simple example of validation with file attached, content type check and custom error message.
Provides RSpec-compatible and Minitest-compatible matchers for testing the validators.
In spec_helper.rb, you'll need to require the matchers:
require 'active_storage_validations/matchers'And include the module:
RSpec.configure do |config|
config.include ActiveStorageValidations::Matchers
endMatcher methods available:
describe User do
# aspect_ratio:
# #allowing, #rejecting
it { is_expected.to validate_aspect_ratio_of(:avatar).allowing(:square) }
it { is_expected.to validate_aspect_ratio_of(:avatar).rejecting(:portrait) }
# attached
it { is_expected.to validate_attached_of(:avatar) }
# processable_image
it { is_expected.to validate_processable_image_of(:avatar) }
# limit
# #min, #max
it { is_expected.to validate_limits_of(:avatar).min(1) }
it { is_expected.to validate_limits_of(:avatar).max(5) }
# content_type:
# #allowing, #rejecting
it { is_expected.to validate_content_type_of(:avatar).allowing('image/png', 'image/gif') }
it { is_expected.to validate_content_type_of(:avatar).rejecting('text/plain', 'text/xml') }
# dimension:
# #width, #height, #width_min, #height_min, #width_max, #height_max, #width_between, #height_between
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).width(250) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).height(200) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).width_min(200) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).height_min(100) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).width_max(500) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).height_max(300) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).width_between(200..500) }
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).height_between(100..300) }
# size:
# #less_than, #less_than_or_equal_to, #greater_than, #greater_than_or_equal_to, #between
it { is_expected.to validate_size_of(:avatar).less_than(50.kilobytes) }
it { is_expected.to validate_size_of(:avatar).less_than_or_equal_to(50.kilobytes) }
it { is_expected.to validate_size_of(:avatar).greater_than(1.kilobyte) }
it { is_expected.to validate_size_of(:avatar).greater_than_or_equal_to(1.kilobyte) }
it { is_expected.to validate_size_of(:avatar).between(100..500.kilobytes) }
# total_size:
# #less_than, #less_than_or_equal_to, #greater_than, #greater_than_or_equal_to, #between
it { is_expected.to validate_total_size_of(:avatar).less_than(50.kilobytes) }
it { is_expected.to validate_total_size_of(:avatar).less_than_or_equal_to(50.kilobytes) }
it { is_expected.to validate_total_size_of(:avatar).greater_than(1.kilobyte) }
it { is_expected.to validate_total_size_of(:avatar).greater_than_or_equal_to(1.kilobyte) }
it { is_expected.to validate_total_size_of(:avatar).between(100..500.kilobytes) }
end(Note that matcher methods are chainable)
All matchers can currently be customized with Rails validation options:
describe User do
# :allow_blank
it { is_expected.to validate_attached_of(:avatar).allow_blank }
# :on
it { is_expected.to validate_attached_of(:avatar).on(:update) }
it { is_expected.to validate_attached_of(:avatar).on(%i[update custom]) }
# :message
it { is_expected.to validate_dimensions_of(:avatar).width(250).with_message('Invalid dimensions.') }
endTo use the matchers, make sure you have the shoulda-context gem up and running.
You need to require the matchers:
require 'active_storage_validations/matchers'And extend the module:
class ActiveSupport::TestCase
extend ActiveStorageValidations::Matchers
endThen you can use the matchers with the syntax specified in the RSpec section, just use should validate_method instead of it { is_expected_to validate_method } as specified in the shoulda-context gem.
- verify with remote storages (s3, etc)
- verify how it works with direct upload
- add more translations
To run tests in root folder of gem:
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_6_1_4.gemfile bundle exec rake testto run for Rails 7.0BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_0.gemfile bundle exec rake testto run for Rails 7.0BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_1.gemfile bundle exec rake testto run for Rails 7.1BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_2.gemfile bundle exec rake testto run for Rails 7.2BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_8_0.gemfile bundle exec rake testto run for Rails 8.0
Snippet to run in console:
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_6_1_4.gemfile bundle
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_0.gemfile bundle
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_1.gemfile bundle
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_2.gemfile bundle
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_8_0.gemfile bundle
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_6_1_4.gemfile bundle exec rake test
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_0.gemfile bundle exec rake test
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_1.gemfile bundle exec rake test
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_7_2.gemfile bundle exec rake test
BUNDLE_GEMFILE=gemfiles/rails_8_0.gemfile bundle exec rake testTips:
- To focus a specific test, use the
focusclass method provided by minitest-focus - To focus a specific file, use the TEST option provided by minitest, e.g. to only run size_validator_test.rb file you will execute the following command:
bundle exec rake test TEST=test/validators/size_validator_test.rb
You are welcome to contribute.
- https://github.com/schweigert
- https://github.com/tleneveu
- https://github.com/reckerswartz
- https://github.com/Uysim
- https://github.com/D-system
- https://github.com/ivanelrey
- https://github.com/phlegx
- https://github.com/rr-dev
- https://github.com/dsmalko
- https://github.com/danderozier
- https://github.com/cseelus
- https://github.com/vkinelev
- https://github.com/reed
- https://github.com/connorshea
- https://github.com/Atul9
- https://github.com/victorbueno
- https://github.com/UICJohn
- https://github.com/giovannibonetti
- https://github.com/dlepage
- https://github.com/StefSchenkelaars
- https://github.com/willnet
- https://github.com/mohanklein
- https://github.com/High5Apps
- https://github.com/mschnitzer
- https://github.com/sinankeskin
- https://github.com/alejandrodevs
- https://github.com/molfar
- https://github.com/connorshea
- https://github.com/yshmarov
- https://github.com/fongfan999
- https://github.com/cooperka
- https://github.com/dolarsrg
- https://github.com/jayshepherd
- https://github.com/ohbarye
- https://github.com/randsina
- https://github.com/vietqhoang
- https://github.com/kemenaran
- https://github.com/jrmhaig
- https://github.com/evedovelli
- https://github.com/JuanVqz
- https://github.com/luiseugenio
- https://github.com/equivalent
- https://github.com/NARKOZ
- https://github.com/stephensolis
- https://github.com/kwent
- https://github.com/Animesh-Ghosh
- https://github.com/gr8bit
- https://github.com/codegeek319
- https://github.com/clwy-cn
- https://github.com/kukicola
- https://github.com/sobrinho
- https://github.com/iainbeeston
- https://github.com/marckohlbrugge
- https://github.com/Mth0158
- https://github.com/technicalpickles
- https://github.com/ricsdeol
- https://github.com/Fonsan
- https://github.com/tagliala
- https://github.com/ocarreterom
- https://github.com/aditya-cherukuri
- https://github.com/searls
- https://github.com/yenshirak
- https://github.com/wataori
- https://github.com/Scorpahr
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.