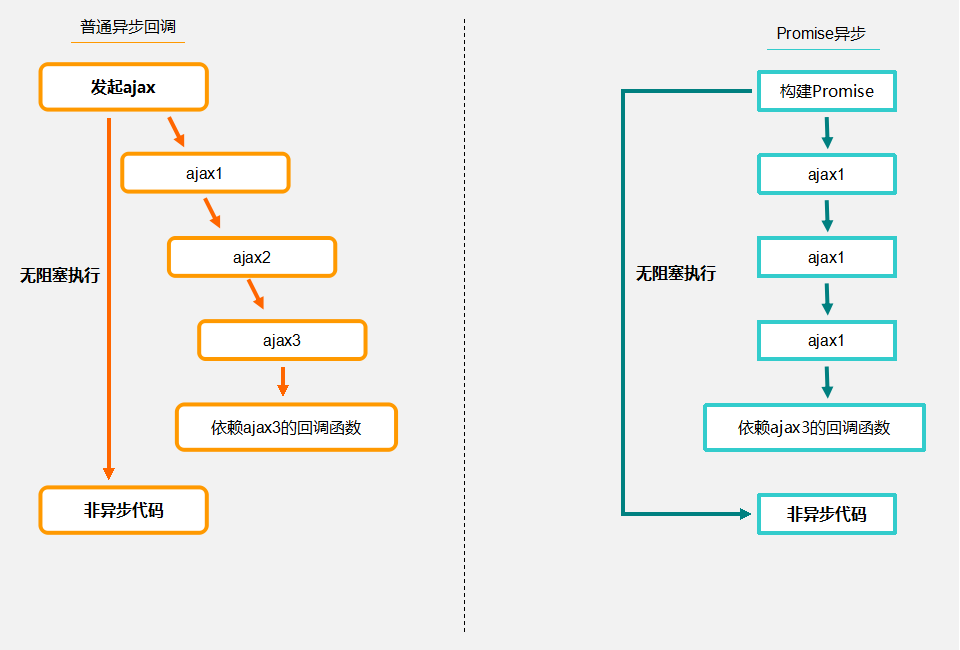
Promise-polyfill兼容库Promise.js,tests/promise.html目录下文件里覆盖了完整的API单元测试。
##什么是Promise?
Promise对象用于延迟(deferred) 计算和异步(asynchronous ) 计算。一个Promise对象代表着一个还未完成,但预期将来会完成的操作。Promise用来传递异步操作的消息。它代表了某个未来才会知道结果的事件(通常是一个异步操作),并且这个事件提供统一的API,可供进一步处理。
Promise对象是一个返回值的代理,这个返回值在Promise对象创建时未必已知。它允许你为异步操作的成功(fulfilled)或失败(rejected)指定处理方法。 这使得异步方法可以像同步方法那样返回值:异步方法会返回一个包含了原返回值的Promise对象来替代原返回值。
Promise对象有以下几种状态:
- pending: 初始状态, 非 fulfilled 或 rejected.
- fulfilled: 成功的操作.
- rejected: 失败的操作.
Promise在JavaScript语言早有实现,饱受三年的争议,最终纳入ECMAScript 2015(ECMAScript 6)规范,Promise遵循Promise/A+规范。统一了用法,原生提供了Promise对象。
当前或古老的浏览器环境并不完全支持Promise,于是我编写了这个polyfill的库,用于兼容当前的浏览器环境。
Promise的经典在于将JavaScript异步编程抹平为同步编程。
更多的Promise API细节请参阅我的文章《JavaScript异步编程(1)- ECMAScript 6的Promise对象》(我肯定要把我的文章单独放啦~~).
更多相关文章:
- 《ECMAScript 6入门 - Promise对象》
- Promise/A+规范
- Promise/A+规范(翻译)
- JavaScript Promise启示录
- [译]深入理解Promise五部曲:1. 异步问题
演示加载一张图片
var imgLoad = function (src, success, error) {
var img = new Image();
img.onload = function () {
success('done');
}
img.onabort = img.onerror = function () {
error('fail');
};
img.src = src;
};
//调用
imgLoad('foo.jpg',
function (str) {
console.log(str, '成功');//=> 'done 成功'
},
function (str) {
console.log(str, '失败');//=> 'fail 失败'
});Promise实现
var imgLoad = function (src) {
//返回Promise
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
var img = new Image();
img.onload = function () {
resolve('done')
}
img.onabort = img.onerror = function () {
reject('fail');
};
img.src = src;
});
};
//调用
imgLoad('foo.jpg')
//异步逻辑抹平
.then(function (str) {
console.log(str, '成功');//=> 'done 成功'
}, function (str) {
console.log(str, '失败');//=> 'fail 失败'
});或者利用它可以把异步的代码封装的更加扁平化:
//过去的代码:异步回调地狱
foo.getJSON('/foo?bar=0', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=1', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=2', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=3', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=4', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=5', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=6', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=7', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=8', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=9', function () {
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=10', function () {
console.log('done');
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
});
//Promise封装之后
$.getJSON('/foo?bar=0')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=1')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=2')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=3')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=4')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=5')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=6')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=7')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=8')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=9')
.getJSON('/foo?bar=10')
.then(function () {
console.log('done');
})
Promise的流程,异步的代码扁平化编写:
promise(ok).then(ok_1).then(ok_2).then(ok_3).reslove(value)------+
| | | | |
| | | | +=======+ |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
+---------|----------|----------|--------→ ok() ←------+
| | | | ↓ |
| | | | ↓ |
+----------|----------|--------→ ok_1()|
| | | ↓ |
| | | ↓ |
+----------|--------→ ok_2()|
| | ↓ |
| | ↓ |
+--------→ ok_3()-----+
| | |
| | ↓
@ Created By Barret Lee +=======+ exit
##特性
- 优雅精湛的实现Promise
- 覆盖原生Promise 95% 以上的API特性和细节
构造函数(constructor)
文档:Promise Object
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {//resolve表示成功,reject表示失败
//异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');//1s后标识成功
}, 1000);
});
Promise.prototype.then()方法返回一个新的Promise。它有两个参数,分别为Promise在 success(成功) 和 failure(失败) 情况下的回调函数
文档:Promise.prototype.then
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');//1s后标识成功
}, 1000);
}).then(function (data) {
//Resolved
console.log(data);//1s后输出foo
//传递结果到下一个链
return 'bar';
}, function () {
//Rejected
}).then(function (data) {
console.log(data);//1s输出foo后,输出bar
})then中的的回调函数可以重写Promise链:
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');//1s后标识成功
}, 1000);
}).then(function (data) {
//Resolved
//重写Promise链
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
reject('bar');
}, 1000);
});
}).then(function () {
//Resolved
}, function (data) {
//Rejected
console.log(data);//2s后,输出bar,
})
Promise.prototype.catch() 方法只处理Promise被拒绝的情况,并返回一个Promise。该方法的行为和调用Promise.prototype.then(undefined, onRejected)相同。
文档:Promise.prototype.catch
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');//1s后标识成功
}, 1000);
}).then(function (data) {
//Resolved
throw Error('bar');
}).catch(function (e) {
//catch接住异常
console.log(e);//1s后输出Eoor:bar
});catch具有冒泡性质,它的Error可以冒泡:
var noop = function () { };
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');//1s后标识成功
}, 1000);
}).then(function (data) {
//Resolved
throw Error('bar');
}).then(noop)//多个Promise链
.then(noop)
.then(noop)
.then(noop)
.catch(function (e) {
//catch接住异常
console.log(e);//1s后输出Eoor:bar
});当Promise中的回调函数抛出异常之后(then/constructor),需要使用catch进行捕获,否则catch会冒泡到全局环境下:
new Promise(function () {
//window Error => Uncaught (in promise) Error: ex => 触发未捕获异常
throw new Error('ex');
});上面的代码会抛出全局异常,而需要使用catch进行捕获,catch的行为和then(null, onRejected)一致,所以也可以使用then(null, onRejected)进行捕获,下面两段代码是相同的的意义(捕获异常):
new Promise(function () {
throw new Error('ex');
}).catch(function (e) {
//Reject
console.log(e);//捕获异常 输出Error: ex
});
//等同于上面的代码
new Promise(function () {
throw new Error('ex');
}).then(function () {
//Resolve
}, function (e) {
//Reject
console.log(e);//捕获异常 输出Error: ex
});
Promise.all(promises) 方法返回一个promise,该promise会在promises参数内的所有promise都被解决后被解决。
文档:Promise.all
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve) {
//异步任务
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');
}, 100);
}), promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('bar');
}, 200);
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2]).then(function (datas) {
//Resolve
console.log(datas);//约200ms以后,输出:['foo', 'bar']
}, function () {
//Rejected
});Promise.race(promises)方法返回一个promise,这个promise在promises中的任意一个promise被解决或拒绝后,立刻以相同的解决值被解决或以相同的拒绝原因被拒绝。
文档:Promise.race
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve) {
//异步任务
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');
}, 100);
}), promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve,reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
reject('bar');//失败
}, 200);
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2]).then(function (datas) {
//Resolve
console.log(datas);//约100ms以后,输出:'foo'
}, function () {
//Rejected
});
Promise.resolve(value)方法返回一个以给定值resolve掉的Promise对象。但如果这个值是thenable的(就是说带有then方法)
返回的promise会“追随”这个thenable的对象,接收它的最终状态(指resolved/rejected/pendding);否则这个被返回的promise对象会以这个值被fulfilled
文档:Promise.resolve
//demo1
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve) {
//异步任务
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('foo');
}, 100);
});
Promise.resolve(promise1).then(function (datas) {
//Resolve
console.log(datas);//约100ms以后,输出:'foo'
}, function () {
//Rejected
});
//demo2
Promise.resolve(true).then(function (data) {
//Resolve
console.log(data);//直接输出true
});
Promise.reject(reason)方法返回一个用value拒绝的Promise。
文档:Promise.reject
Promise.reject(false).then(function (data) {
//Resolve => 不会执行
console.log(data);
}, function (value) {
//Rejected
console.log(value);//直接输出false
});##兼容性
当前仅兼容到支持ECMAScript 5的(现代)浏览器,有需求可以兼容低版本浏览器。
2015-11-16
- 创建了Promise
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2015 linkFly, and a number of other contributors.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.