According to Wikipedia:
In computer science, binary search trees (BST), sometimes called ordered or sorted binary trees, are a particular type of container: data structures that store "items" (such as numbers, names etc.) in memory. They allow fast lookup, addition and removal of items, and can be used to implement either dynamic sets of items, or lookup tables that allow finding an item by its key (e.g., finding the phone number of a person by name).
Binary search trees keep their keys in sorted order, so that lookup and other operations can use the principle of binary search: when looking for a key in a tree (or a place to insert a new key), they traverse the tree from root to leaf, making comparisons to keys stored in the nodes of the tree and deciding, on the basis of the comparison, to continue searching in the left or right subtrees. On average, this means that each comparison allows the operations to skip about half of the tree, so that each lookup, insertion or deletion takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree. This is much better than the linear time required to find items by key in an (unsorted) array, but slower than the corresponding operations on hash tables.
Several variants of the binary search tree have been studied in computer science; this article deals primarily with the basic type, making references to more advanced types when appropriate.
The height of a node is the length of the longest downward path to a leaf from that node. The depth of a node is the length of the path to its root.
- Height and depth of an empty tree: -1
- Height and depth of a tree with just a root node: 0
- Height of the root is the height of the tree.
A full Binary Search Tree (sometimes perfect Binary Search Tree) is a tree in which every node other than the leaves has two children. A complete Binary Search Tree is a Binary Search Tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
The height of the tree equals the number of edges between the root and a leaf. The number of levels equals the height + 1.
Number of nodes: maximum nodes where
levels = height + 1 where height = edges-between-root-and-leaf
- 1 edge, 2 levels =>
nodes N | NN
- 2 edges, 3 levels =>
nodes N | NN | NN NN
- 3 edges, 4 levels =>
nodes N | NN | NN NN | NN NN NN NN
Maximum number of nodes at i level = (level 0 => 1, level 1 => 2, level 2 => 4, level 3 => 8)
- if n nodes, than number of
levels = log(n + 1), depth still levels - 1 - if n nodes, than the
number of edges = n - 1
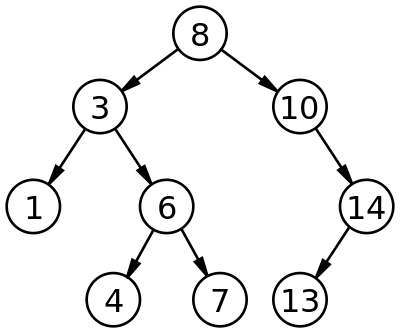
Take a look at the following tree:-
A binary search tree of size 9 and depth 3, with 8 at the root. The leaves are not drawn.
| Operation | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Access | |
| Search | |
| Insertion | |
| Deletion |