| page_title |
|---|
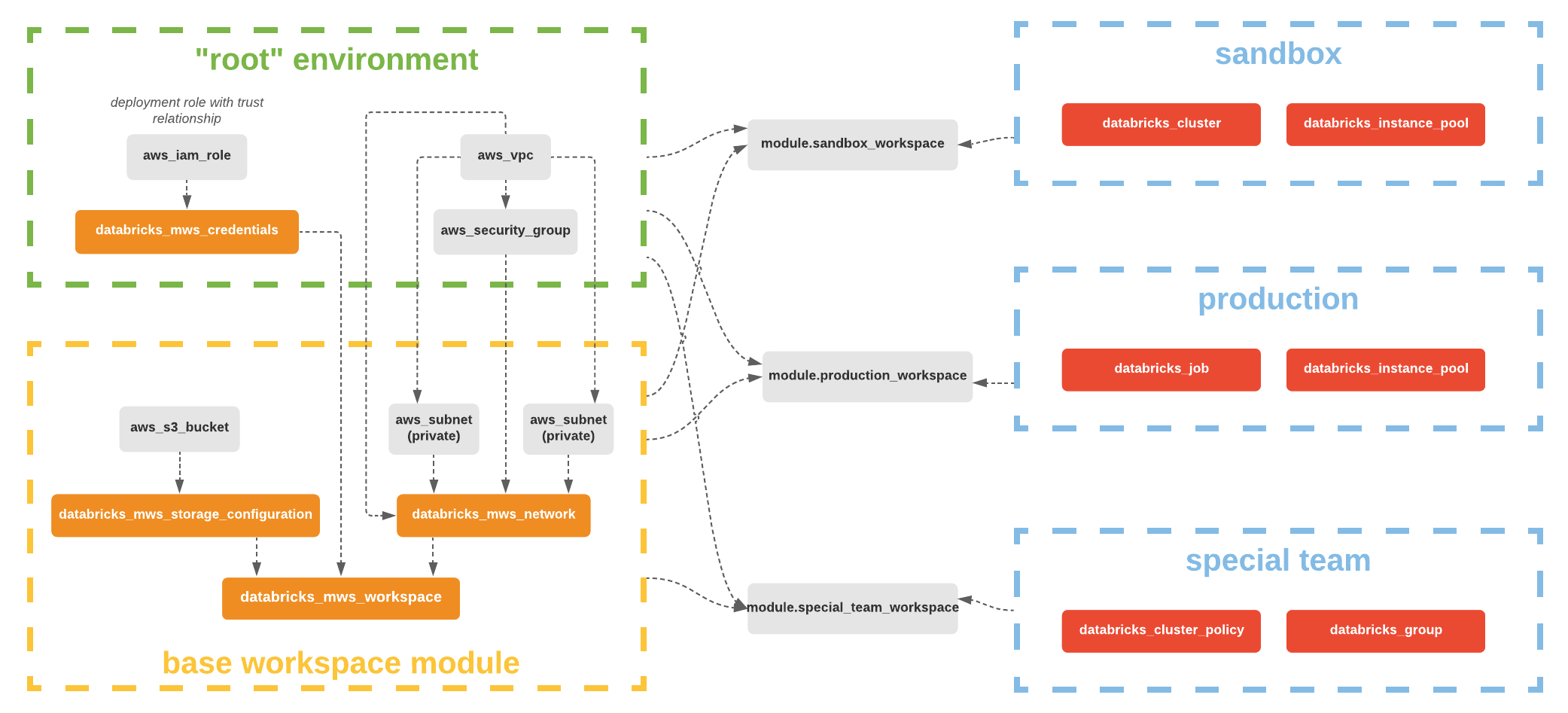
Provisioning AWS Databricks workspace |
-> Note Refer to the Databricks Terraform Registry modules for Terraform modules and examples to deploy Azure Databricks resources.
You can provision multiple Databricks workspaces with Terraform.
This guide assumes you have the client_id, which is the application_id of the Service Principal, client_secret, which is its secret, and databricks_account_id, which can be found in the top right corner of the Account Console. (see instruction). This guide is provided as is and assumes you will use it as the basis for your setup.
variable "client_id" {}
variable "client_secret" {}
variable "databricks_account_id" {}
variable "tags" {
default = {}
}
variable "cidr_block" {
default = "10.4.0.0/16"
}
variable "region" {
default = "eu-west-1"
}
resource "random_string" "naming" {
special = false
upper = false
length = 6
}
locals {
prefix = "demo${random_string.naming.result}"
}Before managing workspace, you have to create:
Initialize provider with
alias = "mws"and useprovider = databricks.mwsfor alldatabricks_mws_*resources. We require alldatabricks_mws_*resources to be created within a dedicated terraform module of your environment. Usually, this module creates VPC and IAM roles as well.
terraform {
required_providers {
databricks = {
source = "databricks/databricks"
}
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.15.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = var.region
}
// initialize provider in "MWS" mode to provision new workspace
provider "databricks" {
alias = "mws"
host = "https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com"
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
client_id = var.client_id
client_secret = var.client_secret
}Cross-account IAM role is registered with databricks_mws_credentials resource.
data "databricks_aws_assume_role_policy" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
external_id = var.databricks_account_id
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "cross_account_role" {
name = "${local.prefix}-crossaccount"
assume_role_policy = data.databricks_aws_assume_role_policy.this.json
tags = var.tags
}
data "databricks_aws_crossaccount_policy" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
policy_type = "customer"
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "this" {
name = "${local.prefix}-policy"
role = aws_iam_role.cross_account_role.id
policy = data.databricks_aws_crossaccount_policy.this.json
}
resource "databricks_mws_credentials" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
role_arn = aws_iam_role.cross_account_role.arn
credentials_name = "${local.prefix}-creds"
depends_on = [aws_iam_role_policy.this]
}The very first step is VPC creation with necessary firewall rules. Please consult main documentation page for the most complete and up-to-date details on networking. AWS VPS is registered as databricks_mws_networks resource. For STS, S3, and Kinesis, you can create VPC gateway or interface endpoints such that the relevant in-region traffic from clusters could transit over the secure AWS backbone rather than the public network for more direct connections and reduced cost compared to AWS global endpoints. For more information, see Regional endpoints.
data "aws_availability_zones" "available" {}
module "vpc" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws"
version = "3.2.0"
name = local.prefix
cidr = var.cidr_block
azs = data.aws_availability_zones.available.names
tags = var.tags
enable_dns_hostnames = true
enable_nat_gateway = true
single_nat_gateway = true
create_igw = true
public_subnets = [cidrsubnet(var.cidr_block, 3, 0)]
private_subnets = [cidrsubnet(var.cidr_block, 3, 1),
cidrsubnet(var.cidr_block, 3, 2)]
manage_default_security_group = true
default_security_group_name = "${local.prefix}-sg"
default_security_group_egress = [{
cidr_blocks = "0.0.0.0/0"
}]
default_security_group_ingress = [{
description = "Allow all internal TCP and UDP"
self = true
}]
}
module "vpc_endpoints" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws//modules/vpc-endpoints"
version = "3.2.0"
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
security_group_ids = [module.vpc.default_security_group_id]
endpoints = {
s3 = {
service = "s3"
service_type = "Gateway"
route_table_ids = flatten([
module.vpc.private_route_table_ids,
module.vpc.public_route_table_ids])
tags = {
Name = "${local.prefix}-s3-vpc-endpoint"
}
},
sts = {
service = "sts"
private_dns_enabled = true
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
tags = {
Name = "${local.prefix}-sts-vpc-endpoint"
}
},
kinesis-streams = {
service = "kinesis-streams"
private_dns_enabled = true
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
tags = {
Name = "${local.prefix}-kinesis-vpc-endpoint"
}
},
}
tags = var.tags
}
resource "databricks_mws_networks" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
network_name = "${local.prefix}-network"
security_group_ids = [module.vpc.default_security_group_id]
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
}Once VPC is ready, create an AWS S3 bucket for DBFS workspace storage, commonly called root bucket. This provider has databricks_aws_bucket_policy with the necessary IAM policy template. The AWS S3 bucket has to be registered through databricks_mws_storage_configurations.
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "root_storage_bucket" {
bucket = "${local.prefix}-rootbucket"
acl = "private"
force_destroy = true
tags = merge(var.tags, {
Name = "${local.prefix}-rootbucket"
})
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_server_side_encryption_configuration" "root_storage_bucket" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.bucket
rule {
apply_server_side_encryption_by_default {
sse_algorithm = "AES256"
}
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "root_storage_bucket" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.id
block_public_acls = true
block_public_policy = true
ignore_public_acls = true
restrict_public_buckets = true
depends_on = [aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket]
}
data "databricks_aws_bucket_policy" "this" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.bucket
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "root_bucket_policy" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.id
policy = data.databricks_aws_bucket_policy.this.json
depends_on = [aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.root_storage_bucket]
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "root_bucket_versioning" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Disabled"
}
}
resource "databricks_mws_storage_configurations" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
bucket_name = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.bucket
storage_configuration_name = "${local.prefix}-storage"
}Once VPC, cross-account role, and root bucket are set up, you can create Databricks AWS workspace through databricks_mws_workspaces resource.
Code that creates workspaces and code that manages workspaces must be in separate terraform modules to avoid common confusion between provider = databricks.mws and provider = databricks.created_workspace. We specify databricks_host and databricks_token outputs, which must be used in the latter modules.
-> Note If you experience technical difficulties with rolling out resources in this example, please make sure that environment variables don't conflict with other provider block attributes. When in doubt, please run TF_LOG=DEBUG terraform apply to enable debug mode through the TF_LOG environment variable. Look specifically for Explicit and implicit attributes lines, which should indicate authentication attributes used. The other common reason for technical difficulties might be related to missing alias attribute in provider "databricks" {} blocks or provider attribute in resource "databricks_..." {} blocks. Please make sure to read alias: Multiple Provider Configurations documentation article.
resource "databricks_mws_workspaces" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
aws_region = var.region
workspace_name = local.prefix
credentials_id = databricks_mws_credentials.this.credentials_id
storage_configuration_id = databricks_mws_storage_configurations.this.storage_configuration_id
network_id = databricks_mws_networks.this.network_id
token {
comment = "Terraform"
}
}
output "databricks_host" {
value = databricks_mws_workspaces.this.workspace_url
}
output "databricks_token" {
value = databricks_mws_workspaces.this.token[0].token_value
sensitive = true
}In Terraform 0.13 and later, data resources have the same dependency resolution behavior as defined for managed resources. Most data resources make an API call to a workspace. If a workspace doesn't exist yet, default auth: cannot configure default credentials error is raised. To work around this issue and guarantee proper lazy authentication with data resources, you should add depends_on = [databricks_mws_workspaces.this] to the body. This issue doesn't occur if a workspace is created in one module and resources within the workspace are created in another. We do not recommend using Terraform 0.12 and earlier if your usage involves data resources.
data "databricks_current_user" "me" {
depends_on = [databricks_mws_workspaces.this]
}In the next step, please use the following configuration for the provider:
provider "databricks" {
host = module.e2.workspace_url
token = module.e2.token_value
}We assume that you have a terraform module in your project that creates a workspace (using Databricks Workspace section) and you named it as e2 while calling it in the main.tf file of your terraform project. And workspace_url and token_value are the output attributes of that module. This provider configuration will allow you to use the generated token to authenticate to the created workspace during workspace creation.
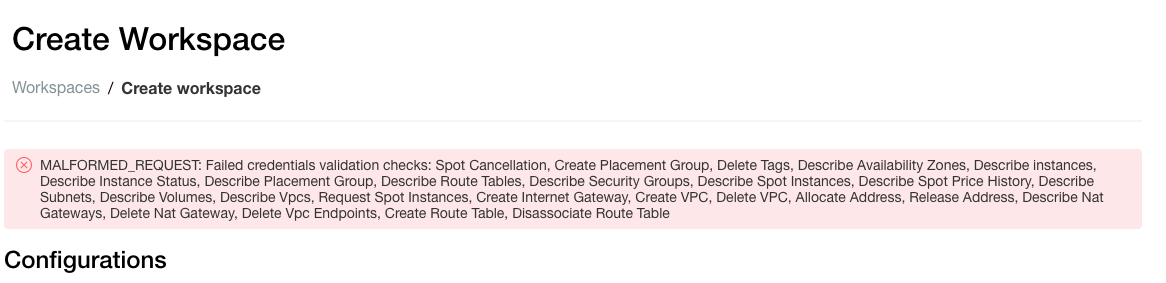
Due to a bug in the Terraform AWS provider (spotted in v3.28) the Databricks AWS cross-account policy creation and attachment to the IAM role takes longer than the AWS request confirmation to Terraform. As Terraform continues creating the Workspace, validation checks for the credentials fail, as the policy isn’t applied more quickly. Showing the error:
Error: MALFORMED_REQUEST: Failed credentials validation checks: Spot Cancellation, Create Placement Group, Delete Tags, Describe Availability Zones, Describe instances, Describe Instance Status, Describe Placement Group, Describe Route Tables, Describe Security Groups, Describe Spot Instances, Describe Spot Price History, Describe Subnets, Describe Volumes, Describe Vpcs, Request Spot Instances
(400 on /api/2.0/accounts/{UUID}/workspaces)As a workaround, give the aws_iam_role more time to be created with a time_sleep resource, which you need to add as a dependency to the databricks_mws_workspaces resource.
resource "time_sleep" "wait" {
depends_on = [
aws_iam_role.cross_account_role]
create_duration = "10s"
}If you notice the below error:
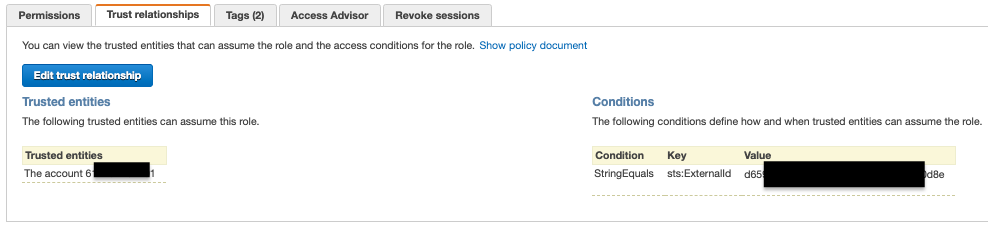
Error: MALFORMED_REQUEST: Failed credentials validation checks: Spot Cancellation, Create Placement Group, Delete Tags, Describe Availability Zones, Describe instances, Describe Instance Status, Describe Placement Group, Describe Route Tables, Describe Security Groups, Describe Spot Instances, Describe Spot Price History, Describe Subnets, Describe Volumes, Describe Vpcs, Request Spot Instances- Try creating workspace from UI:
- Verify if the role and policy exist (assume role should allow external ID)
See the troubleshooting guide