Looking to supercharge your React applications with AI capabilities? Meet OpenAssistant - your new favorite tool for seamlessly integrating AI power into existing React apps without the hassle.
Unlike general-purpose chatbot library, OpenAssistant takes a different approach. It's specifically engineered to be the bridge between Large Language Models (LLMs) and your application's functionality. Think of it as your application's AI co-pilot that can not only chat with users but also execute complex tasks by leveraging your app's features and external AI plugins.
Check out the following examples using OpenAssistant in action:
| kepler.gl AI Assistant (kepler.gl) | GeoDa.AI AI Assistant (geoda.ai) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 🤖 Multiple AI Provider Support
- DeepSeek (Chat and Reasoner)
- OpenAI (GPT models)
- Google Gemini
- Ollama (local AI models)
- 🎯 Advanced Capabilities
- 🌟 AI Assistant Plugins
- DuckDB: in-browser query data using duckdb via prompt
- ECharts: visualize data using echarts via prompt
- GeoDa: apply spatial data analysis using geoda wasm via prompt
- 🎨 Customizable UI Components
- Pre-built chat interface
- Pre-built LLM configuration interface
- Screenshot wrapper for your app
- Theme support
- 📦 Easy Integration
- CLI tool for adding components
- TypeScript support
- Tailwind CSS integration
# Install the core package
npm install @openassistant/core @openassistant/uiimport { AiAssistant } from '@openassistant/ui';
// only for React app without tailwindcss
import '@openassistant/ui/dist/index.css';
function App() {
return (
<AiAssistant
modelProvider="openai"
model="gpt-4"
apiKey="your-api-key"
enableVoice={true}
welcomeMessage="Hello! How can I help you today?"
/>
);
}See the tutorial for more details.
To use the Screenshot to Ask feature, you just need to wrap your app with ScreenshotWrapper and pass the startScreenCapture and screenCapturedBase64 to the AiAssistant component using e.g. redux state. See an example in kepler.gl: app.tsx and assistant-component.tsx.
Below is a simple example.
import { AiAssistant, ScreenshotWrapper } from '@openassistant/ui';
// only for React app without tailwindcss
import '@openassistant/ui/dist/index.css';
function App() {
const [startScreenCapture, setStartScreenCapture] = useState(false);
const [screenCaptured, setScreenCaptured] = useState('');
return (
<>
<ScreenshotWrapper
setScreenCaptured={setScreenCaptured}
startScreenCapture={startScreenCapture}
setStartScreenCapture={setStartScreenCapture}
>
<div className="h-[600px] w-[400px] m-4">
<AiAssistant
modelProvider="openai"
model="gpt-4"
apiKey="your-api-key"
welcomeMessage="Hello! How can I help you today?"
enableVoice={true}
enableScreenCapture={true}
screenCapturedBase64={screenCaptured}
onScreenshotClick={() => setStartScreenCapture(true)}
onRemoveScreenshot={() => setScreenCaptured('')}
/>
</div>
</ScreenshotWrapper>
</>
);
}See the tutorial for more details.
For project with tailwindcss, you can add the following to your tailwind.config.js file:
import { nextui } from '@nextui-org/react';
module.exports = {
content: [
'./src/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}',
'./node_modules/@nextui-org/theme/dist/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}',
'./node_modules/@openassistant/ui/dist/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}',
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
darkMode: 'class',
plugins: [nextui()],
};OpenAssistant provides a new way that allows users to interact with the data and your application in a natural and creative way.
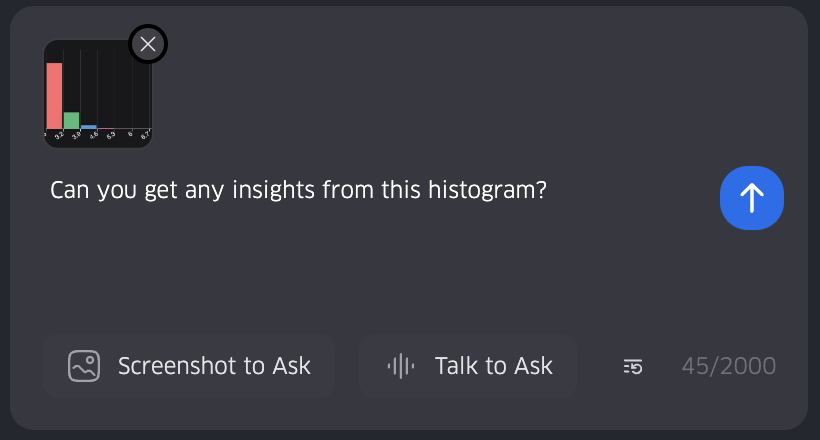
This feature enables users to capture a screenshot anywhere within kepler.gl application and ask questions about the screenshot.
For example:
- users can take a screenshot of the map (or partial of the map) and ask questions about the map e.g.
how many counties are in this screenshot, - or take a screenshot of the configuration panel and ask questions about how to use it, e.g.
How can I adjust the parameters in this panel. - users can even take a screenshot of the plots in the chat panel and ask questions about the plots e.g.
Can you give me a summary of the plot?.
- Click the "Screenshot to Ask" button in the chat interface
- A semi-transparent overlay will appear
- Click and drag to select the area you want to capture
- Release to complete the capture
- The screenshot will be displayed in the chat interface
- You can click the x button on the top right corner of the screenshot to delete the screenshot
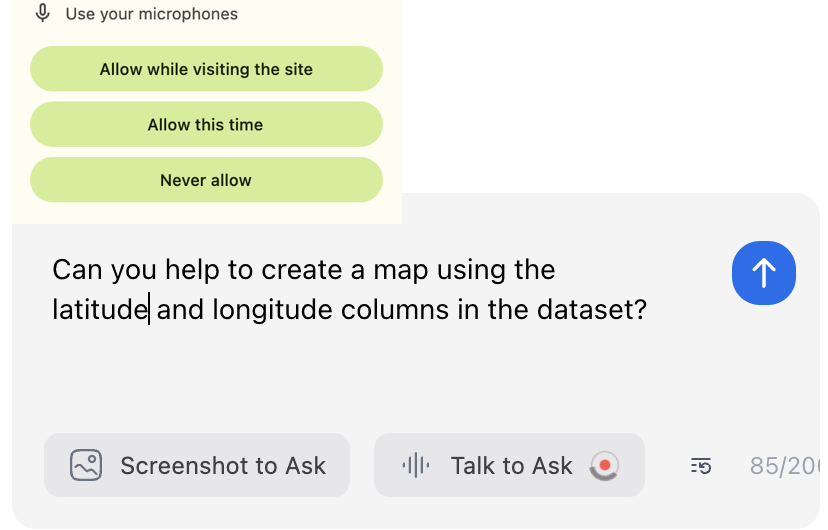
This feature enables users to "talk" to the AI assistant. After clicking the "Talk to Ask" button, users can start talking using microphone. When clicking the same button again, the AI assistant will stop listening and send the transcript to the input box.
When using the voice-to-text feature for the first time, users will be prompted to grant microphone access. The browser will display a permission dialog that looks like this:
After granting access, users can start talking to the AI assistant.
Function calling enables the AI Assistant to perform specialized tasks that LLMs cannot handle directly, such as complex calculations, data analysis, visualization generation, and integration with external services. This allows the assistant to execute specific operations within your application while maintaining natural language interaction with users.
Yes, the data you used in your application stays within the browser, and will never be sent to the LLM. Using function tools, we can engineer the AI assistant to use only the meta data for function calling, e.g. the name of the dataset, the name of the layer, the name of the variables, etc. Here is a process diagram to show how the AI assistant works:
OpenAssistant provides great type support to help you create function tools. You can create a function tool by following the tutorial here.
OpenAssistant also provides plugins for function tools, which you can use in your application with just a few lines of code. For example,
- the DuckDB plugin allows the AI assistant to query your data using DuckDB. See a tutorial here.
- the ECharts plugin allows the AI assistant to visualize data using ECharts. See a tutorial here.
- the Kepler.gl plugin allows the AI assistant to create beautiful maps. See a tutorial here.
- the GeoDa plugin allows the AI assistant to apply spatial data analysis using GeoDa. See a tutorial here.
- @openassistant/ui: Pre-built chat UI components
- @openassistant/core: Core functionality and hooks
- @openassistant/cli: CLI tool for adding components to your project
- @openassistant/duckdb: DuckDB integration for data querying
- @openassistant/geoda: GeoDa integration for spatial data analysis
- @openassistant/echarts: ECharts integration for data visualization
Add the chat components to your React project:
npx add-ai-chatThe CLI will help you set up the components and required dependencies.
Your project have these dependencies:
- react
- @langchain/core
- @langchain/google-genai
- @langchain/ollama
- @langchain/openai
- html2canvas
- next-themes
- @nextui-org/react
- framer-motion
For detailed documentation and examples, visit our package-specific READMEs:
Check out our example projects:
MIT © Xun Li